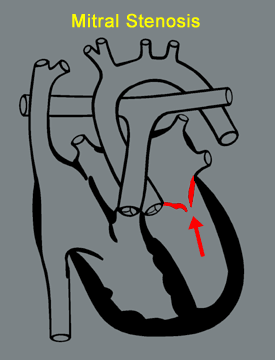
 (rollover to compare with normal)
(rollover to compare with normal) |
|
What Are Its Effects?
The abnormal mitral valve results in increased blood pressure in the left atrium and in the lungs, which send oxygen-rich blood to the left atrium.
The symptoms of Mitral Stenosis may be absent or very slight for long periods. However, they may gradually or suddenly worsen. If the narrowing of the valve orifice becomes severe, blood will back up into the lungs resulting in pulmonary hypertension, and right sided heart failure.
The adverse symptoms that can be caused by Mitral Stenosis often appear at times of stress, such as during strenuous exertion, in conjunction with a fever (when the heart pumps more vigorously), or when one is experiencing powerful emotions, such as fear. These symptoms may include tiredness, lack of energy, difficulty breathing or shortness of breath, heart palpitations, flushed cheeks, and a persistent cough, sometimes producing blood. |